A few examples of stochastic processes from physics and biology
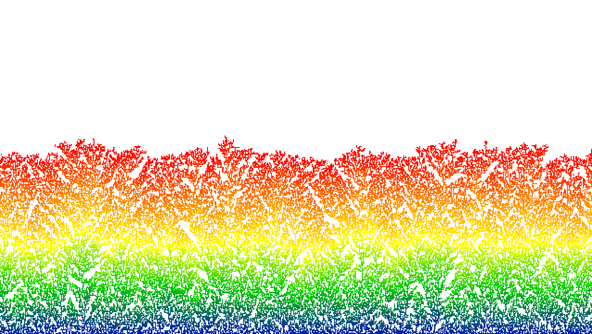
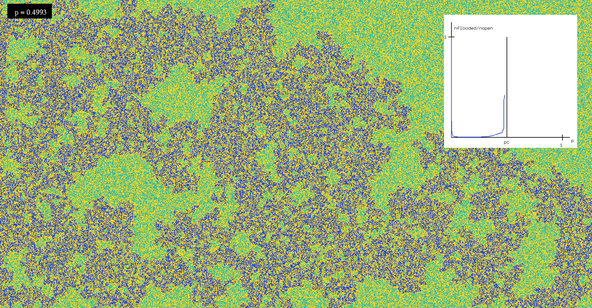
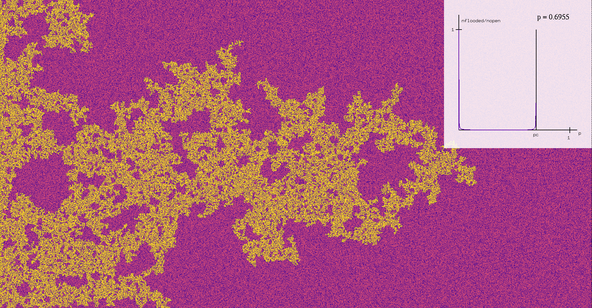
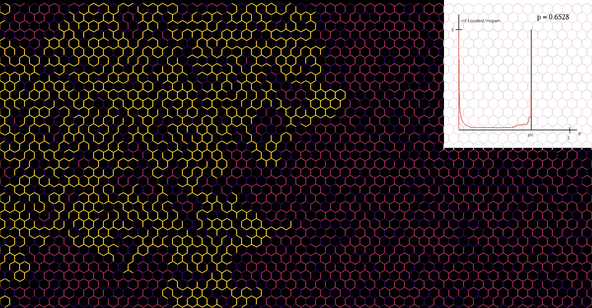
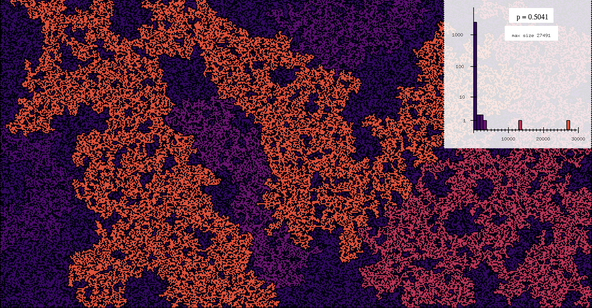
The images in this gallery are mostly simulations of stochastic processes, arising from applications in statistical physics or in biology. A stochastic process is a process evolving in time in a random way. Thus it can also be seen as a family of random variables indexed by time. Typical examples are the size of a population, the boundary between two phases in an alloy, or interacting molecules at positive temperature.
The programs generating these images have been coded directly in C, which is used to produce eps files, which can then be translated into other formats. There are also a couple of related movies in the films section.
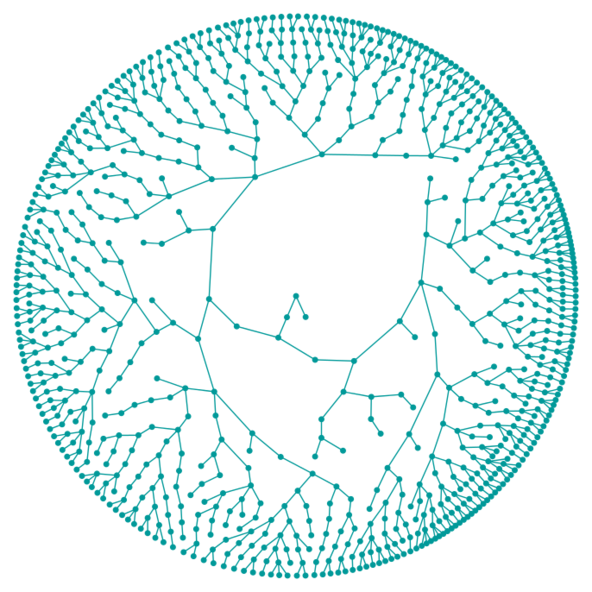
Galton-Watson tree
A realisation of a Galton-Watson tree. The ancestor, in the center of the picture, has two children. Each individual has again a random number of children (between 0 and 3 in this simulation), all children numbers being independent and identically distributed.
Une réalisation d’un arbre de Bienaymé-Galton-Watson. L’ancêtre, au centre de l’image, a deux enfants. Chaque individu a à nouveau un nombre aléatoire d’enfants (entre 0 et 3 dans cette simulation), tous les nombres d’enfants étant indépendants et identiquement distribués.
Pour une explication détaillée, voir http://images. math. cnrs.fr/La-probabilite-d-extinction-d-une.html